Sinus Infection (Sinusitis): Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
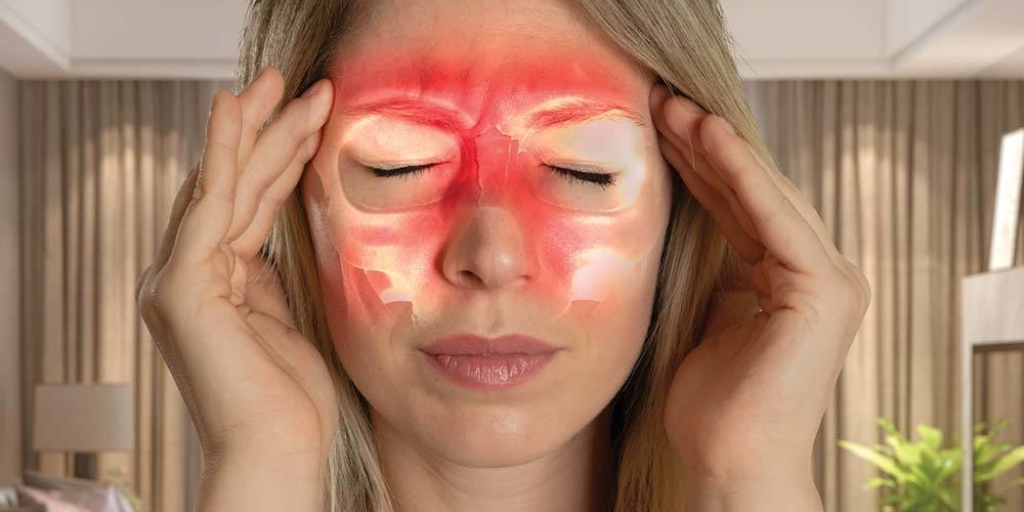
What Is Sinusitis?
Sinusitis is inflammation, swelling, or infection of the tissue that lines the sinuses. Your sinuses are a group of hollow cavities in your skull which are all interconnected. The tissue inside the sinus cavities is called mucosa. Typically the sinuses have nothing except a thin layer of mucus. However, a sinus infection occurs when a virus, bacteria, or some type of fungus causes inflammation or infection inside the cavity.
The sinuses that lie across the lower center of your forehead are called the frontal sinuses. The cavities between your eyes are called the ethmoid sinuses. Just inside the ethmoid sinuses, on either side of your nose, are the sphenoid sinuses. Your maxillary sinuses are held in your cheekbones and are the largest sinus cavities.
Who Gets a Sinus Infection?
You, me, everybody! Sinus infections are common and anyone can develop one due to viral illnesses and other infectious diseases.
You may be at a higher risk of getting a sinus infection if you suffer from allergies or have asthma. The nasal passages have natural defenses, but allergies may cause them to overreact. Then itchy eyes, sneezing, and mucus production all increase. Exposure to smoke, as well as changes in air pressure from things like air travel, swimming, or scuba diving, can also increase your risk. You may also be more likely to get a sinus infection if you have a compromised immune system.
Symptoms of Sinusitis
Most of us know the symptoms of a sinus infection all too well. A case of sinusitis usually includes a number of the most common symptoms listed below. Remember, if these symptoms last more than 10 days, contact your healthcare provider.
- nasal congestion or a stuffy nose
- nasal discharge or runny nose or post-nasal drip
- facial pressure or facial pain (especially where the sinuses are located)
- headache
- fever
- fatigue
- cough
- sore throat
- bad breath
Acute Sinusitis and Chronic Sinusitis
Inflammation and infection of the sinuses that typically last anywhere between 1-4 weeks is considered acute sinusitis. Often the result of the common cold, the flu, or other viruses, the symptoms of acute sinusitis closely resemble those of the viral illness. However, acute sinusitis occurs when the inflammation spreads to the sinus cavities and the mucosal tissue that lines the sinuses becomes infected.
Chronic sinusitis is persistent inflammation of the sinuses, that does not respond to the standard treatments for acute sinusitis. Simply having recurring viral sinus infections over various seasons does not constitute chronic sinusitis. Allergies may contribute to chronic sinusitis. Nasal polyps (small growths on the lining of your nasal passages) also contribute to chronic sinusitis.
How is a Sinus Infection Diagnosed?
A doctor typically starts with a visual examination, using a light to look inside the nasal passages for swelling, redness, increased mucus, and other signs of infection. Your doctor may also press on your face to see if there is pain in the areas of the sinuses. This examination along with a description of your symptoms may be enough for a doctor to diagnose a sinus infection, or suggest other medications to relieve symptoms.
Chronic sinusitis may require more work to diagnose. A CT scan if often used to provide detailed imaging of the sinuses. Your doctor may also take a sinus culture to evaluate a sample of the mucus or tissue inside the sinuses. A rhinoscopy allows a doctor to insert a tube with a tiny camera in order to inspect the inside of your nose and sinuses. These procedures are typically only done when another treatment has failed, or sinusitis has become chronic.
Treatment for Sinusitis
Treatment for sinus infections starts at home. Rest well and drink lots of water—staying hydrated helps keep mucus thin so it doesn’t get trapped and become infected. You can use saline nasal sprays, nasal rinses or nasal irrigation (such as a neti pot) to reduce symptoms like nasal discharge and pressure. You can also make yourself more comfortable by putting warm compresses on your forehead and nose. This will help relieve sinus pressure. Over-the-counter medications such as Tylenol and Ibuprofen may help with the symptoms of fever, pain, and headache.
If your symptoms get worse, go away and then return, or last more than 10 days, see a healthcare provider. Urgent care facilities, like TrustCare, can provide quick convenient care without the long wait. A doctor may instruct you to take over-the-counter or prescription medications that fall into these categories:
- Decongestants: As the name suggests, these medications decrease congestion and the pressure caused by congestion.
- Antihistamines: These medications can help to dry out nasal discharge, especially if it is caused by allergies.
- Cough suppressants: Coughing can be important in order to keep the infection from spreading to the respiratory tract and to keep the lungs clear of mucus. However, severe coughing is uncomfortable! Cough suppressants may be used to control and decrease coughing. This is especially helpful if coughing has become dry, asthmatic, or is keeping you from resting.
- Expectorants: These medications help to keep mucus thin, which helps reduce the chance of infection. Your doctor may prescribe an expectorant anytime a cough suppressant is used. This combination helps to avoid mucus that doesn’t move and becomes thick and more susceptible to infection.
Depending on the length or severity of your symptoms, your doctor may also prescribe antibiotics to help rid your body of a bacterial infection. Remember, an illness caused by a virus that does not involve a secondary infection will not benefit from antibiotics. So talk with your doctor about the best treatment for your symptoms. Steroids may also be prescribed to help reduce tissue swelling, to help treat related breathing issues, or to prevent the growth of nasal polyps.
In extreme cases of chronic sinusitis, treatment may include corticosteroids, allergy shots, removal of nasal polyps, or sinus surgery.
What Happens if Sinusitis Isn’t Treated?
The reality is that most cases of sinusitis will clear up on their own. If the duration and severity indicate a bacterial infection, your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic. Despite the misery of the symptoms, when left untreated, a sinus infection will usually heal thanks to time and your body’s amazing immune system. However, when a sinus infection lasts longer than 10 days, it’s a good idea to consult your doctor. Not only can doctors provide solutions to ease your discomfort, but they can also make sure there are no other complications from the infection. In rare cases an infection can spread, causing life-threatening conditions like brain abscess or meningitis. Complications around the eyes can also result in reduced vision or blindness.
When to See a Doctor
Acute sinusitis can take a long time to clear up, typically lasting 1-4 weeks. So grab your tissues, hot tea, and a good book. However, if your symptoms haven’t improved after a week to 10 days, you should see a doctor. You should also see a healthcare provider if your symptoms get worse, you develop a high fever, or you notice swelling or discharge around your eyes. TrustCare provides the fastest and most convenient way to get treatment for a sinus infection. The doctors and staff at all of TrustCare’s locations are here to help you feel better.
We have several urgent care clinics in the Jackson metro area and Hattiesburg. You can visit our urgent care clinics on a walk-in basis, or contact us to make a future appointment.
